User:Rpeters: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
(bootable USB) |
||
| (200 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
= Projector = |
|||
Be aware that projectors and monitors have two fundamental differences as external displays |
|||
'''this is it''' |
|||
*The majority of projectors, particularly those oriented to "home theatre" are still manufactured with 4:3 ratio display generators |
|||
-[[User:Rpeters|Rpeters]]13:25, 24 August 2012 (EST) |
|||
*projectors have many fewer megapixels than do laptops and medium to large monitors |
|||
--[[Category:Technical Info]] |
|||
;def:definition list |
|||
;:def:definition list |
|||
== For General Users == |
== For General Users == |
||
Virtually any computer having two display outputs can be made to drive two displays (whether monitor(s) or projector(s) - '''after a fashion''' |
|||
=== Overview === |
|||
*occasional users should get adequate result by following the simple guidelines below |
|||
Advanced Format (AF) Hard Disk Drives are used in many pre-built computers and USB drives from about 2011 onwards.. By way of explanation |
|||
*regular users might want to follow the more technical guidelines to try to optimise the displays somewhat |
|||
*AF drives have 4 kB hard sectors in lieu of |
|||
*the traditional 512 B sectors |
|||
Now the bad news: |
|||
==== Advantages ==== |
|||
The potential combinations of hardware and software capabilities are huge. |
|||
*much faster (less disk overhead) |
|||
*more space efficient (larger disk capacity from same hardware) |
|||
*overcomes immutable capacity limit of ~2.19 TeraByte for conventional drives |
|||
==== Disadvantages ==== |
|||
*Windows 32 bit systems cannot boot from AF drives |
|||
**requires driver from HDD manufacturer, to use as data only internal drives |
|||
No action is required by the typical purchaser, because the manufacturer will have taken care of the special formatting required with AF drives. ''Getting Technical'' below, provides guidelines for those needing to: |
|||
Additionally, flat panel displays, whether generated via LCD, LED or DLP, produce clearest display only at their native resolution |
|||
*repartition drives |
|||
*install new, "bare" drives |
|||
* |
|||
=== Projectors for Presentations === |
|||
Image clarity is paramount for still images as used with presentations |
|||
*the human eye cannot resolve high resolution images at the distance typically used with projection screens |
|||
#ascertain the aspect ratio of the projector |
|||
*if documentation is not available, the ratio of the plain, white image produced when a computer is not connected is a good guide. |
|||
#ascertain the native resolution of the projector. In the absence of documentation: |
|||
*1024 x768 is typical for 4:3 ratio projectors |
|||
*1280 x 800 is typical for 16:10 ratios |
|||
*1280 x 720 is typical for 16:9 ratios |
|||
#from the computer's Control Panel go to Display and set: |
|||
*resolution to same a projector |
|||
*tick the box "duplicate/clone these displays" |
|||
#click "save" and the desktop should be duplicated on the projector |
|||
Display on the laptop/PC will be less than optimum |
|||
*"wide-screen" displays may have unlit areas at sides of display |
|||
*may be less clear as a result of lower resolution |
|||
The above are unavoidable compromises to obtaining clearest display on the projector |
|||
==== Common Problems ==== |
|||
*display on the projector is a plain desktop wallpaper without icons or windows for apps |
|||
**This is caused by not having the displays duplicated |
|||
**revisit Display setup on the computer |
|||
*"wide-screen" display on a 4:3 ratio projector |
|||
**this is a faulty configuration, which results in less clear display and needs to be corrected |
|||
**revisit Display setup on the computer |
|||
**if still not corrected, this likely results from default settings in the projector |
|||
#activate projector's on-screen display |
|||
#navigate to aspect ratio |
|||
#change from "auto" or 16:9 to 4:3 |
|||
First the good news: |
|||
Virtually any computer having two display outputs can be made to drive two displays (whether monitor(s) or projector(s) - '''after a fashion''' |
|||
Now the bad news: |
|||
The potential combinations of hardware and software capabilities are huge. |
|||
*occasional users should get adequate result by following the simple guidelines below |
|||
*regular users might want to follow the more technical guidelines to try to optimise the displays somewhat |
|||
Be aware that projectors and monitors have two fundamental differences as external displays |
|||
#The majority of projectors, particularly those oriented to "home theatre" are still manufactured with 4:3 ratio display generators |
|||
#projectors have many fewer megapixels than laptops and medium to large monitors |
|||
=== Projectors for Presentations === |
|||
==== Preliminary Configuration for Laptops ==== |
|||
=== Projectors for Presentations === |
|||
=== Projectors for Home Theatre Use === |
|||
The majority are still 4:3 native ratio |
|||
*but have the capability to accept 16:9 ratio input, typically to support movies |
|||
**many default to this ratio and require no reconfiguration |
|||
**will display 16:9 ratio input via "letterboxing", ie blanking out the top & bottom 100 or so rows of pixels and displaying image in reduced size |
|||
***uses more than the native number of pixels and causes some reduction in image clarity |
|||
***which is not significant for movies |
|||
***but noticeable with still images (as in presentations) |
|||
Up-market projectors are now being manufactured with 16:9 ratio display generators |
|||
== Getting Technical == |
== Getting Technical == |
||
=== Advanced Format Drives === |
|||
New HDD from about 2011 onwards are likely to be Advance Formatted |
|||
*usually pre-formatted |
|||
*likely to be stated on drive or packaging |
|||
*essential for drives over 2.1 TeraByte capacity |
|||
*has been used on new drives as small as 250GB |
|||
Be aware that 3 ratios are in common use for displays - 4:3 and 16:9 for consumer grade devices plus business grade monitors & projectors that support the 16:10 wide-screen ratio |
|||
Avoid reformatting drives to MBR |
|||
*better quality 16:9 and 16:10 displays might present the complete, alternative image correctly via blanking some rows or columns of pixels with slight "letterboxing" or blank right & left margins |
|||
*performance loss of up to 40% if reformatted MBR |
|||
*others will distort the image slightly to occupy the full visible area |
|||
*requires special procedure - see "Strictly for Geeks" below |
|||
. |
|||
A new type of partition table called Globally Unique Identifier(GUID) Partition Table (GPT) is required to optimise the performance of AF disks. The partition table previously in common use has no univerwsally agreed name but is given the nomenclature |
|||
Master Boot Record (MBR), because that was a unique feature of it. |
|||
All digital displays, whether LCD, LED, Plasma or DLP provide the sharpest image only at their native resolution |
|||
Legacy partitioning tools do not handle GPT. A suitable tool for intermediate users is "parted" or its GUI front-end "gparted". The simplest way to use these is from a bootable utility CD |
|||
Linux & iOS support different resolutions on the two displays |
|||
http://www.sysresccd.org/Download |
|||
*low end hardware might not support this well, if at all |
|||
http://partedmagic.com/doku.php?id=downloads |
|||
*if the resolutions selected have differing vertical resolutions on the two displays, then the bottom panel used by many desktops will be absent on the shorter display |
|||
**might need to compromise with either |
|||
***identical vertical resolutions or |
|||
***setting the primary display to the higher vertical resolution |
|||
== Strictly for Geeks == |
|||
It is not advisable to delete or alter patitions of type ef01 or ef02, because these have a special purpose in GPT. Other partitions may be re-sized or added, as required. Note that: |
|||
*all partitons in GPT are Primary |
|||
*up to 128 primaries are permitted |
|||
*GPT has no concept of "Extended" or "Logical" partitions. |
|||
*partition type numbers sometimes differ from those used with MBR partition tables |
|||
A compleat description of GPT is available at: |
|||
== For General Users == |
|||
http://www.rodsbooks.com/gdisk |
|||
The idea of having both Windows and Linux installed on a computer and being able to select one at boot time appeals to many who are trying, or migrating to, Linux. |
|||
=== New Drives === |
|||
*Windows own bootloader cannot boot Linux |
|||
**a Linux bootloader must be used with dual-booting |
|||
The better known Linux distributions will set this up automatically, during installation to a '''single''' hard disk drive in the computer |
|||
The full capacity of Drives over 2.1 TB can be utilised only via recent mainboards or add-on SATA controllers |
|||
*<span style="color:#ef2108; background:#black">''' It is likely to cease functioning following the next update of Windows'''</span> and |
|||
*support for SATA 3 (aka 6 Gb/sec) is required |
|||
**restoring dual-boot requires Getting Technical |
|||
The boot flag in GPT does *not* make a disk bootable from a BIOS mainboard. See the procedures at: |
|||
Keep at least one emergency boot medium handy. See [[Emergency_Boot - Including for Dual-Boot]] |
|||
http://www.sysresccd.org/Sysresccd-Partitioning-EN-The-new-GPT-disk-layout |
|||
== Getting Technical == |
|||
The above problem can usually be obviated by having additional hard disk(s) in the computer. This is not an expensive option, given current HDD prices. |
|||
=== USB Drive === |
|||
==== Pros ==== |
|||
*easily added |
|||
*no change to internal HDD |
|||
==== Cons ==== |
|||
*Linux relies on the absolute order of storage devices detected by the computer's firmware |
|||
**plugging in (say) a uSB memory drive, may upset the booting |
|||
**many bootloaders will identify partitions via UUID, to overcome this limitation |
|||
=== Internal HDD === |
|||
*ensures permanent order of drives |
|||
=== Installation === |
|||
*mainstream Linux will allow installation to== Strictly for Geeks == a second HDD |
|||
=== Selecting Boot Device === |
|||
The selection of "drive" and hence OS is done at POST stage and depends on type of firmware in the computer |
|||
see [[Booting from Removable Media]] |
|||
== Strictly for Geeks == |
== Strictly for Geeks == |
||
=== Capacity === |
|||
The international standard for data capacity uses multipliers of 2 ^ 10 in lieu of SI decimal multipliers of 10 ^ 3 eg |
|||
*kiB = 1024 Bytes |
|||
*kB = 1000 Bytes |
|||
through |
|||
*TiB = 2.198 TB |
|||
*the bootloader must also be installed to the second HDD, in this technique |
|||
Why does this matter ? |
|||
**can require "drilling down" the installation options |
|||
#drives have always had sectors that are multiples of kiB |
|||
#*0.5 kiB for conventional HDD |
|||
#*2 kiB for CD & some Magneto Optics |
|||
#*4 kiB for AF drives |
|||
#*32 kiB for DVD |
|||
#advanced formatting tools allocate partitions in MiB, GiB, TiB increments |
|||
#*partition sizes will be reported larger by older OS |
|||
#*formatted capacity of a drive will be somewhat '''less''' than manufacturer's nameplate rating, which is usually in decimal |
|||
#advanced formatting tools might align partitions on MiB boundaries |
|||
#*helps optimise performance |
|||
=== Tools === |
|||
A more capable partitioning tool is required to set up the advanced features of GPT. The partitioning tool '''gdisk''' is downloadable from |
|||
http://www.rodsbooks.com/gdisk/download.html |
|||
=== Partition Conversion === |
|||
MBR drives can be converted to GPT partition table, without erasing data, subject to some limitations and risks |
|||
*essential to backup data & system files |
|||
*use the "r" menu option in gdisk, followed by "g" |
|||
*some partition numbers might be changed |
|||
--[[User:Rpeters|Rpeters]]11:28, 24 August 2012 (EST) |
|||
=== Advanced Patitioning Layouts === |
|||
--[[Category:Technical Info]] |
|||
*non-sequential partition numbering |
|||
== Bootloaders == |
|||
*spaces between partitions |
|||
*partition alignment on 1 MiB boundaries |
|||
=== Elilo === |
|||
Only for computers having EFI firmware |
|||
Fairly simple and reliable |
|||
==== Re-formatting ==== |
|||
*but requires a running Linux to generate its config file, in advance |
|||
Drives up to 2.1 TB,manufactured during the transitional period, logically divide each 4kB sector into eight 512 B sectors |
|||
*permits partitioning using legacy programs |
|||
*deprecated because doing so can decrease performance up to 40% |
|||
**essential for boot drives in Windows 32 bit systems |
|||
=== GRUB Legacy (aka 0.97 ) === |
|||
AF drives that are re-formatted to MBR might behave unreliably unless expert options in gdisk are used |
|||
*see "z" menu option |
|||
A simple, reliable bootloader, although being phased out and no longer maintained. Use situations: |
|||
== File Migration == |
|||
The simplest approach is to install additional HDD '''before''' any systems are installed or data created. If that is not feasible then any existing files/folders at the intended mount point need to be migrated |
|||
#ensure that the files to be migrated are firstly backed up to independent media |
|||
#as user root mount the new partition to a temporary point, typically /mnt/ |
|||
#cd to the mount point that will later be used permantly for the new partition |
|||
#use the "cp -ax" command to copy all files from within the folder of the mount point to ./mnt |
|||
#*do not use use file managers for this purpose, because those may set incorrect timestamps, permisisons etc for files |
|||
#unount from the temporary point |
|||
#set the permanent mount point (and change permissions, if necessary) as in sections "User Storage" or "System Storage" below |
|||
#the above procedure '''duplicates''' existing files. To remove the originals: |
|||
#*temporarily '''unmount''' the new partition |
|||
#*delete all files in the folder of the permanent mount point |
|||
#*remount the new partition to its permanent mount point |
|||
*have only Linux on /ext(n) partitions and (maybe) Windows |
|||
=== GRUB (aka GRUB 2 ) === |
|||
== Firewalls == |
|||
GRUB 2 is now the most frequently used bootloader in Linux, but has many remaining issues. Some work-arounds: |
|||
== Packet-Filtering v Router == |
|||
a perenniel question is whether it is preferable to run a packet-filtering style firewall on '''each''' workstation/laptop/pocket-PC or to use a '''single''' "hardware" router to protect the whole LAN |
|||
=== |
==== "on-the-fly" Mode ==== |
||
GRUB 2 relies on a pre-defined config file /boot/grub(2)/grub.cfg. If this is not located, for any reason, GRUB 2 may boot to a grub> prompt. To boot from here use the following commands, substituting relevant drive and partition numbers: |
|||
==== Advantages ==== |
|||
*no additional hardware, cost, wattage |
|||
*zero acreage |
|||
::grub> set root='hd0,gpt10' |
|||
==== Disadvantages ==== |
|||
::grub> linux /boot/vmlinuz root=/dev/sda10 |
|||
*generally less "hardened" |
|||
::grub> initrd /boot/initrd |
|||
**many more background prolcesses need to be running to support user apps |
|||
::grub> bootBlockquote</blockquote |
|||
== Linux == |
|||
Most Linux include a packet-filtering style firewall |
|||
*usually activated, by default |
|||
**but '''check''' |
|||
*efficacy likely to be similar |
|||
**based on iptables |
|||
**may also include ip6tables and ebtables |
|||
*administrative interface specific to distribution |
|||
**"Guarddog" in KDE provides consistent interface |
|||
notes |
|||
== Mac OSX == |
|||
*drive numbers start from 0 |
|||
citation needed |
|||
*must specify whether partitioned mbr or gpt |
|||
== Windows == |
|||
*set root refers to location of partition containing /boot for the operating system to be booted |
|||
citation needed |
|||
**which will often also be the root file system for Linux |
|||
=== Gateway/Router === |
|||
**or merely the system partition for Win |
|||
*generally regarded as "abandon-ware" by manufacturers - typically |
|||
**partition numbers start from 1 (unlike in GRUB legacy) |
|||
**updates are not announced |
|||
*this procedure is easiest if kernel & initrd have easily remembered names |
|||
**only a few updates provided |
|||
**either soft-link generic names or |
|||
**for about three years only |
|||
**press TAB to see possible names |
|||
*ctrl-x or F10 may be pressed in lieu the "boot" command |
|||
The above procedure may be modified to cater for the situation where the menu '''is''' presented but the desired OS is not included or fails to boot. either |
|||
== Firewalls == |
|||
*press e to edit a menu item or |
|||
*press Esc to get to command line, then proceed as above. |
|||
==== Menu mode ==== |
|||
== Packet-Filtering v Router == |
|||
a perenniel question is whether it is preferable to run a packet-filtering style firewall on '''each''' workstation/laptop/pocket-PC or to use a '''single''' "hardware" router to protect the whole LAN |
|||
=== Packet-Filtering === |
|||
See GRUB 2 downloadable manual or use "info grub2" to obtain details. |
|||
==== Advantages ==== |
|||
Consistent themes amongst various documentation for GRUB 2 are that: |
|||
*no additional hardware, cost, wattage |
|||
*zero acreage |
|||
*it is unreliable beyond the basics |
|||
==== Disadvantages ==== |
|||
*OS-probe module is particularly so |
|||
*generally less "hardened" |
|||
*not putting bootstrap in MBR (protective MBR in case of GPT) will |
|||
**many more background prolcesses need to be running to support user apps |
|||
be problematic |
|||
== Linux == |
|||
Most Linux include a packet-filtering style firewall |
|||
*usually activated, by default |
|||
**but '''check''' |
|||
*efficacy likely to be similar |
|||
**based on iptables |
|||
**may also include ip6tables and ebtables |
|||
*administrative interface specific to distribution |
|||
**"Guarddog" in KDE provides consistent interface |
|||
Indeed, "info grub2" recommends avoid all automated installs & configs by |
|||
== Mac OSX == |
|||
distro. Instead, manually grub2-install then write a simple, static |
|||
citation needed |
|||
/boot/grub2/grub.cfg. See below for outline of this procedure. |
|||
== Windows == |
|||
citation needed |
|||
=== Gateway/Router === |
|||
Although these are typically a separate hardware item they are not necessarily an '''additional''' hardware item, often being combined with an ethernet switch and/or DSL modem |
|||
==== Advantages ==== |
|||
*generally more "hardened" |
|||
**by eliminating many background prolcesses that are not needed to support user apps |
|||
*'''single''' point of installation, configuration and update |
|||
As of Jan 2014 and following application of two patches to GRUB in openSUSE 13.1, its GRUB has been brought to ver 2.00-39.4.1. The |
|||
automated process works well enough for most Linux plus Windows |
|||
It failed to find ArchLinux - which uses unusual names for kernels & initrd. |
|||
Simple work-around for that is to add a 90_persistent section at the end of |
|||
/boot/grub2/grub.cfg |
|||
<nowiki>### BEGIN /etc/grub.d/90_persistent ###</nowiki> |
|||
menuentry 'ArchLinux (<your descriptor>) { |
|||
set root='hd<n>,gpt<n>' |
|||
linux /boot/vmlinux-linux root=/dev/sd<x><n> |
|||
initrd /boot/initramfs-linux.img |
|||
} |
|||
<nowiki>### END /etc/grub.d/90_persistent ###</nowiki> |
|||
Essentially, the 90_persistent section gets copied verbatim during any |
|||
subsequent manual or automated run of grub2-mkconfig. Note that this feature might be unique to openSUSE |
|||
The curly braces are essential and enclose GRUB2 commands. |
|||
This was for a HDD partitioned GPT. replace partition number with mbr<n> if |
|||
applicable. |
|||
Multiple menuentries could be put in 90_persistent to cope with multiple |
|||
Linuxes. |
|||
� |
|||
It's also possible to add an entry by pressing "c". In this mode only the 3 |
|||
commands are input, followed by a fourth command 'boot'CTL-x at the |
|||
Someone asked how to increase the font size in boot menu. The manual |
|||
grub.cfg essentially does that by using whatever font will fit on the http://www.pcug.org.au/info/index.php?title=User:Rpeters&action=submit#on |
|||
in GRUB legacy. press 'e' to edit an entry. |
|||
It's also possible to add an entry by pressing "c". In this mode only the 3 |
|||
commands are input, followed by a fourth command 'boot'CTL-x at the |
|||
Someone asked how to increase the font size in boot menu. The manual |
|||
grub.cfg essentially does that by using whatever font will fit on the |
|||
default screen resolution. Alternatively, one could try to make sense of |
|||
the "loadfont" parameters in /etc/grub.d/00_header. |
|||
Wheras GRUB legacy uses similar syntax in command and menu mode, GRUB 2 uses somewhat different syntax in the two modes. |
|||
==== Rescue mode ==== |
|||
An ISO image can be prepared, that is tailored to the OS on a specific computer. See above documentation for details on preparation of this image. It can be tested by "dd" to a USB memory device. |
|||
=== ReFind === |
|||
Only for computers having EFI firmware |
|||
*a CD can be downloaded, to test, if uncertain of firmware |
|||
default screen resolution. Alternatively, one could try to make sense of |
|||
the "loadfont" parameters in /etc/grub.d/00_header. |
|||
Wheras GRUB legacy uses similar syntax in command and menu mode, GRUB 2 uses somewhat different syntax in the two modes. |
|||
==== Rescue mode ==== |
|||
An ISO image can be prepared, that is tailored to the OS on a specific computer. See above documentation for details on preparation of this image. It can be tested by "dd" to a USB memory device. |
|||
=== ReFind === |
|||
Only for computers having EFI firmware |
|||
*a CD can be downloaded, to test, if uncertain of firmware |
|||
=== Syslinux === |
|||
A proven bootloader, that continues being developed and maintained. Main limitations: |
|||
*can't directly boot programs on other than its own partition, resulting in the need for work-arounds: |
|||
**either chain load all but one OS or |
|||
**put the boot code for each OS in a different sub-directory on the syslinux partition |
|||
== DOS USB == |
|||
=== For General Users === |
|||
==== Purpose ==== |
|||
The main requirement for a USB memory device that boots to DOS operating system arises when a BIOS/Firmware update of a computer is required. |
|||
It is advisable to use a new, or little used memory device, because any error in reading the BIOS/Firmware code during the actual update is likely to result in an unusable computer. USB "thumb" drives could be used. SD cards, which can be removed and stored in a secure place, might be more applicable. |
|||
==== Procedure ==== |
|||
HP provide two techniques for producing DOS USB sticks. Both place utility software on a Windows computer, in order to generate the bootable stick - see "Getting Technical" below, if Windows is not available. |
|||
Instructions are provided on the HP support site for installing these utilities to Windows and creating bootable USB stick(s) |
|||
*HP's generic utility HPUSBFW is not self contained but is more flexible. |
|||
**it produces a mimimal DOS bootable USB stick containing only nnnDOS.SYS & COMMAND.COM |
|||
**the user can then add relevant firmware and flashing utility |
|||
**although it has an option for formatting to FAT 32 only FAT actually works |
|||
**requires one of HP's "Softpacs" (firmware updates) for one of their recent commercial notebooks, from which to obtain the Windows utility program, plus |
|||
**also requires FreeDOS (which can be downloaded at no cost in the form of fd11src.iso from http://www.freedos.org/download/) |
|||
*those wanting to upgrade the firmware in a HP computer might find the second tool more suitable. HP provide some of their firmware updates as Windows dotEXE files, which: |
|||
**install a utility program to Windows and then have facility called ROMPAQ for creating a bootable DOS on a USB device of not greater than 2 GB (FAT 16) |
|||
**automatically adds the firmware and flashing utility to the USB stick |
|||
**the naming convention for these files is SPnnnnn.exe |
|||
Note that in order to use the former, generic technique, general users would need to burn the above ISO image to CD. Those not familiar with ISO images should read http://www.pcug.org.au/info/index.php/Using_dotISO_Files |
|||
The step of burning the ISO image can be avoided - see "Getting Technical" below |
|||
=== Getting Techhnical === |
|||
The techniques above contain the Windows version of Syslinux in the Windows software package and install the former as a bootloader on the USB device. The Syslinux bootloader can also be added to a USB memory device via Linux. Generic instructions are at the following site, from which (superceded versions of) the code are also available |
|||
http://goebelmeier.de/bootstick/ |
|||
The following would need to be downloaded to obtain up-to-date software: |
|||
http://www.freedos.org/download/fd11src.iso |
|||
https://www.kernel.org/pub/linux/utils/boot/syslinux/6.xx/ |
|||
Syslinux will already be installed on many Linux systems. However, Ubuntu and openSUSE might produce a USB stick that invokes graphics at boot time and it is undesirable to have superfluous code on a device that will be used for firmware upgrades. |
|||
FreeDOS supports FAT 32 and consequently the above procedure should also work on FAT 32 formatted sticks of > 2 GB capacity. |
|||
'''''PRINTING VIA NETWORK''''' |
|||
'''PRINTING VIA CUPS''' |
|||
== Overview == |
|||
CUPS is not applicable to Windows. Windows users see [[Printing via Network]] |
|||
CUPS now the default print sub-system in most Operating Systems - Android, ChromeOS, MacOS, Linux and BSD. |
|||
Its use can enable printing over a LAN to be achieved relatively simply, often requiring: |
|||
*no additional installation of software or "drivers" |
|||
*only simple configuration changes |
|||
== Applicability == |
|||
=== Android & iOS === |
|||
Typically these require an App to be downloaded from the relevant Store and connect with WiFi enabled printers. |
|||
=== Linux & OSX === |
|||
Both use CUPS and can be configured as below. |
|||
==== Disadvantages ==== |
|||
*possible additional hardware, cost, wattage |
|||
*update support for commercial units is typically infrequent and limited-term |
|||
zero acreage |
|||
== Linux == |
|||
Most Linux include a packet-filtering style firewall |
|||
*usually activated, by default |
|||
== Gateway/Router == |
|||
== For General Users == |
== For General Users == |
||
=== Definitions === |
|||
The relative advantages of a separate gateway/router are discussed at |
|||
Those acquainted with client/server model can skip to sub-item "CUPS Versioning Issues" |
|||
*"client computer" means the computer/device from which the print job will be generated |
|||
*it must have CUPS client installed, which is the default condition for Max OSX and Linux |
|||
*it need not have any printer drivers installed |
|||
**indeed, it is less confusing if it does not |
|||
*"server computer" means the computer controlling the printer. It can be: |
|||
A packaged commercial uint is the most suitable option |
|||
*for network printers, which are connected directly to a network, any computer on the network, having the relevant CUPS print drivers installed |
|||
*ADSL modem/router for ADSL users |
|||
**network may be wired, WiFi or bluetooth |
|||
*"broadband" roiuter for other connection types |
|||
**it is perfectly acceptable to configure several computers to use a particular network printer |
|||
**as of 2012, a router for dial-up connections appears to be unavailable |
|||
*for USB/parallel attached printers, the computer to which the printer is attached |
|||
**it must have CUPS server installed, which is the default condition for Max OSX and Linux |
|||
**the relevant printer must appear in its "Printers" list, and be working |
|||
**the computet must be posered on, to enable printing, although logon won't usually be required . |
|||
=== Prerequisites === |
|||
This guide assumes that CUPS is installed and generally functioning on both computers. The screen shots are from CUPS version 1.4.x/1.5.x. Versions 1.6 et seq have similar menus, but fewer options, with some changes having to be effected via computer's Control Panel instead. |
|||
=== CUPS Versioning Issues === |
|||
== Disadvantages == |
|||
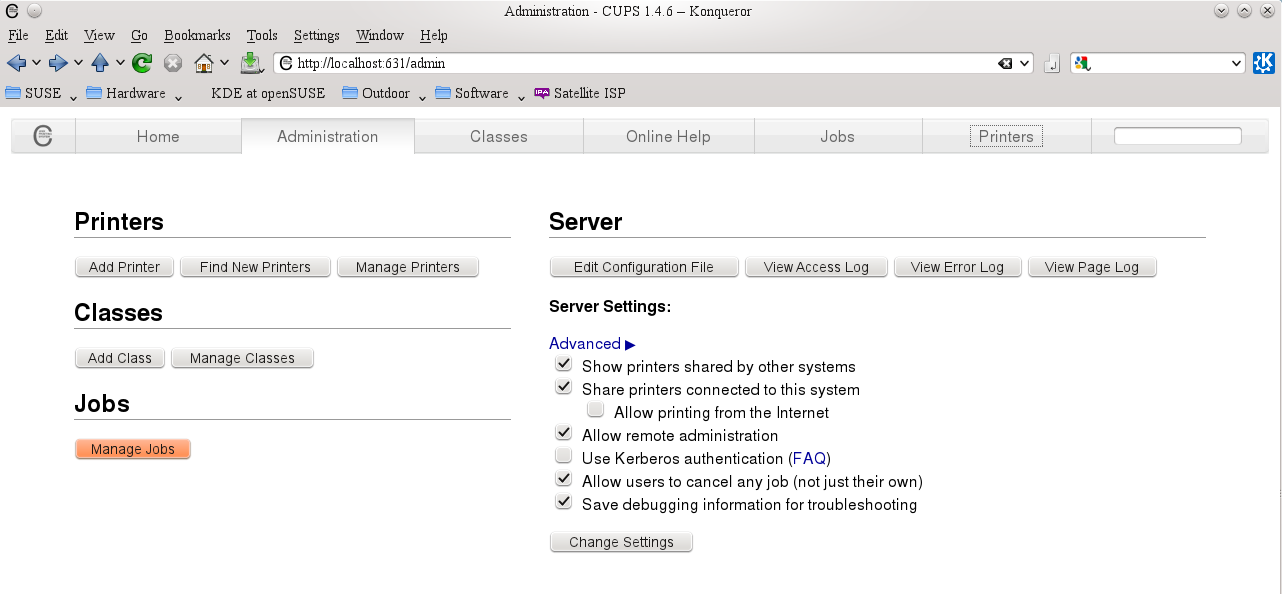
Firstly it is essential to ascertain which release of CUPS is in use, because versions 1.6 and later are largely incompatible with earlier releases. If uncertain, then on '''each''' machine involved in the network printing browse to: |
|||
*generally regarded as "abandon-ware" by manufacturers - typically |
|||
https://localhost:631/admin |
|||
**updates are not announced |
|||
[[Image:Cups_printers_listing.png]] |
|||
**only a few updates provided |
|||
**for about three years only |
|||
*firewalling functions eg SPI, often default to DISABLED |
|||
**apparently to ensure that it "just works" |
|||
**ensure that these functions are re-configured to ENABLED |
|||
the release number should be displayed in the title bar |
|||
== Recommendations == |
|||
*CUPS <= 1.5.4 uses substantially different process from 1.6 and later |
|||
**printing between machines mixing these versions is complicated. see below for guidelines, if unavoidable |
|||
**as CUPS <= 1.5.4 is now used mainly in older OS, there is a case for upgrading the OS on such machines to a current release. |
|||
***it is not feasible for General Users to upgrade the version of CUPS '''without''' upgrading the whole OS |
|||
*CUPS 1.6 and later |
|||
*Devices sold by Apple Inc can deploy proprietary extensions to CUPS. Consequently, some features may not work as expected, if the print job is sent to a printer that is controlled by another version of CUPS |
|||
As a general rule, the print server should have a version not earlier than the client |
|||
A commerical uint that overcomes the above disadvantages ''at a price'' is the FritzBox |
|||
*available from http://www.internode.on.net |
|||
*note that the upmarket model is required to support IPv6 |
|||
=== CUPS mixed networks <= 1.5.4 plus 1.6 et seq === |
|||
A much lower pirced unit is the DLink DIR-615 |
|||
Network printing in this environment is more complex. For a guide to procedures see: |
|||
*this is a broadband router only (no modem) |
|||
http://doc.opensuse.org/release-notes/x86_64/openSUSE/Leap/42.1/ |
|||
Sample screen images displayed in the following sections are similar for CUPS 1.4 and later. |
|||
== Getting Technical == |
|||
=== CUPS 1.6 and later === |
|||
DIY routers overcome the support limitations of commercial units, although until recently this has been at a cost of: |
|||
Later releases of CUPS impose greater network security. Default settings vary with system and may require some troubleshooting if client and server have different origin. |
|||
*acreage |
|||
*wattage |
|||
*additional terminology |
|||
The following client systems automatically discover network printers, from default configurations |
|||
Most DIY units have been based on superceded PC. Additional hardware will be required: |
|||
*Linux Mint 17.3 |
|||
*modem (if not provided by ISP as modem or Set Top Box) |
|||
*openSUSE Leap |
|||
*ethernet switch (unless only one computer will be accessing the Internet) |
|||
*openSUSE Tumbleweed |
|||
*WiFi Access Point |
|||
**if required |
|||
Other environments may require changes For a quick test, from the client computer, open any page in a browser or editor and select "Print" |
|||
**might be implemented as a PCI/PCIe WiFi card in the routing PC |
|||
*if any of the networked printers can be selected then no further configuration is required |
|||
**if not then: |
|||
==== |
====Temporary Fix ==== |
||
The following procedure is adequate for portable machines that are away from home base. It might also suffice for other computers that are rarely used to print. |
|||
Minimum suggested specs are approximately |
|||
*does not require Admin privileges on most systems |
|||
*CPU - any X86 compatible of 333 Mhz or faster |
|||
*but '''does require ''' IP address or host name of the machine sharing printers |
|||
**ARM CPU may now be viable in lieu x86 compatible see "Strictly for Geeks" below |
|||
*settings '''cannot''' be saved |
|||
*RAM - 256 MB |
|||
**additional functions, particularly caching, require extra RAM |
|||
*storage - 2 GB |
|||
**effective caching requires several GB more disk space |
|||
*network interfaces |
|||
**PCI, PCIe or USB-Ethernet required |
|||
**10 Mb/s suffice - unless running ADSL 2 or faster link |
|||
**'''NB''' - speed of other devices on the LAN is irrelevant, LAN performance depends on the ethernet switch deployed |
|||
Wattage for DIY has been somewhat higher than for commerical routers. A suitable objective, using 2010 or later componentry is 25 W. Lower wattage units are addressed under "Strictly for Geeks" below. CPU wattage is a poor indicator because other chips and peripherals consume somewhat more. Suggested basis for low wattage router: |
|||
#HP Proliant Microserver |
|||
#mainboards based on C50 CPU - which appears to have been used only in netbooks |
|||
#mainboards based on E350 CPU |
|||
#mainboards based on Atom CPU are something of an enigma |
|||
#*can be the lowest cost available but |
|||
#*wattage surprisingly high, because of associated chips |
|||
#mainboards based on VIA CPU |
|||
#*expensive unless s/hand |
|||
#*not particularly low wattage |
|||
#mainboards based on Pentium III CPU |
|||
#*reliability might be reduced because of age |
|||
#*zero cost & acceptable wattage |
|||
==== Software ==== |
|||
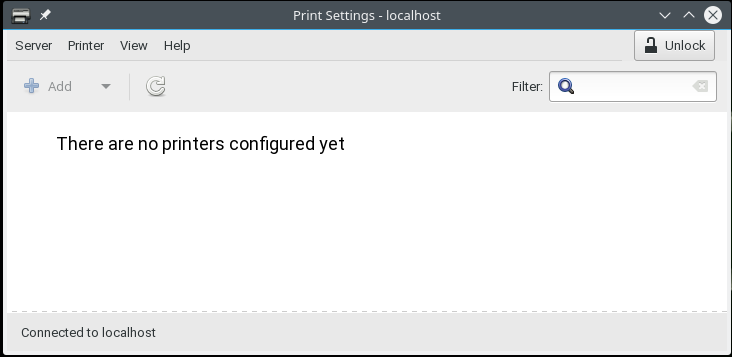
[[Image:Print_Settings_Applet.png |left|frame|]]The Print Settings applet is usually accessible from the main menu and typically has the icon at left |
|||
Many Linux and BSD can be configured a gateway-router, but it is generally simpler and more watt efficient to use a specialised firewall/gateway distribution. Better known ones are listed in [[Linux_Distribution_Recommendations]] Although BSD based distributions such as Monowall are quite functional, their use would involve an additional learning curve for most people |
|||
Start this applet to get its main window as below |
|||
[[Image:Print_settings_localhost.png |none]] |
|||
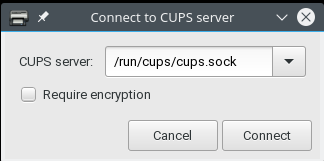
Pull down the Server tab and select Connect, to get the following pop-up dialog |
|||
[[Image:CUPS_server_connect.png |left]] |
|||
Change the name of the server to hostname |
|||
or IP address of that required and click on Connect |
|||
From the client computer, open any page in a browser or editor and select "Print" |
|||
*if any of the networked printers can be selected then no further configuration is required |
|||
**if not then: |
|||
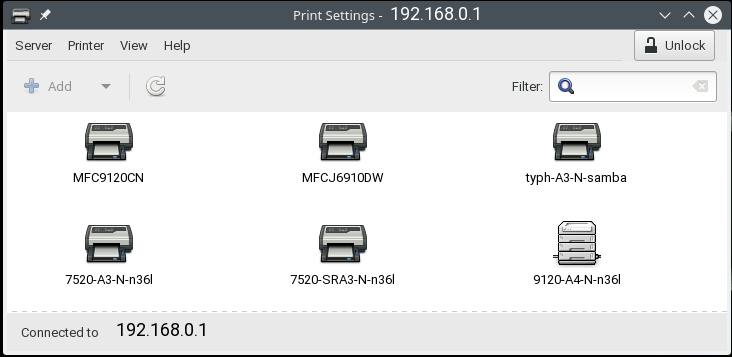
Main window should now display all discovered printers on the network |
|||
[[Image:Print_settings_discovered.png |none|frame]] |
|||
From the client computer, open any page in a browser or editor and select "Print" |
|||
*if any of the networked printers can be selected then no further configuration is required |
|||
**if not then: |
|||
If printers are discovered then any newly opened app eg LibreOffice, browsers, editors etc should be able to select and print to one of the printers |
|||
If no printers are discovered then changes in configuration are required, as below |
|||
==== Retained Configuration ==== |
|||
Neither of the two tools widely deployed for administering CUPS are able to make permanent changes to printer discovery. Both amend the same underling config files: |
|||
*system-config-printer (aka Print Settings) |
|||
*the URL https://<localhost or URL>:631 |
|||
Some of the changes required below need to be made by editing conf files and executing commands at a terminal |
|||
=== Summary of Changes === |
|||
Several settings might need to be changed to print via network - in summary: |
|||
*amend firewall settings, on both ends, if necessary |
|||
**firewall on router should '''not''' be altered |
|||
*set client to use printers shared by another machine on the network |
|||
**in many installations this suffices to get printing working via network |
|||
*activate cups-browsed service via system services (systemd) on both ends |
|||
**only in deployments using this separate service |
|||
*set CUPS on server to share printers but only to the local network |
|||
**often the default setting |
|||
It might pay to configure the client computer first, because other machines are often set to share their printers to the local network. |
|||
*must be done via Control Panel or a combination of editing files then executing commands |
|||
The Print Settings applet typically has the icon [[Image:Print_Settings_Applet.png | Print_Settings_Applet]] |
|||
From the client computer, use "Control Panel" to set the following, if available (exact menus and terminology will vary): |
|||
*firewall on server must have port 631 open |
|||
*configure "Printers" to use network printers |
|||
**note that in many Control Panel apps this item is merely a link the applet "Print Settings", which does not allow changes to print server to be retained. |
|||
In cases where Print Settings is the only tool available: |
|||
*temporary changes to select print server can be made from the applet |
|||
*permanent changes need to be made manually, as follows: |
|||
#modify "system services" (exact terminology will vary) |
|||
*enable '''and''' activate "cups-browsed" |
|||
**not identified as a separate service in some distro (and then not required) |
|||
#modify the file /etc/cups/client.conf**does not require a web browser, which might not be present on a server |
|||
*on many systems this will '''not''' exist by default, but creating it, pointing to a valid IP address that is sharing printers, is usually sufficient to enable the client to use shared printers. Only one line is required in this file: |
|||
<nowiki>ServerName <IP address of machine sharing printers></nowiki> |
|||
*one only servername is used |
|||
**where multiple appear the '''last''' is used |
|||
**many systems default to "localhost" or /var/run/cups/cups.sock |
|||
***can be retained, provided not the last listed |
|||
**does not require a web browser, which might not be present on a server |
|||
Some distro are issued as specific desktop (client) or server releases. The desktop releases might not provide for changed settings to be saved. That allows eg a laptop away from its home base to print, without disturbing longer term settings. |
|||
From the server computer, use "Control Panel" to set the following, if available (exact menus and terminology will vary): |
|||
==== Zoning ==== |
|||
*firewall on server must have port 631 open |
|||
Software for DIY routers implements similar network zoning to that in commercial routers. An aspect that is different is the colour coding of zones: |
|||
*modify "system services" (exact terminology will vary) |
|||
**enable '''and''' activate "cups-browsed" |
|||
***not identified as a separate service in some distro (and then not required) |
|||
From the server computer, use any browser to https://localhost:631/admin |
|||
*<span style="color:#c93800">'''RED'''</span> for untrusted/unfiltered Internet |
|||
*<span style="color:#004700">'''GREEN'''</span> for most trusted, '''wired''' LAN connections |
|||
and activate radio buttons to: |
|||
*<span style="color:#blue">'''BLUE'''</span> for less trusted WiFi connections |
|||
*Share printers connected to this system |
|||
*<span style="color:#magenta">'''PURPLE'''</span> for additional LAN zone |
|||
**using protocols DNSSD & CUPS |
|||
*<span style="color:#orange">'''ORANGE'''</span> for Demilitarized Zone, (DMZ) |
|||
*restrict sharing to "Local Network" |
|||
**not required by most home users |
|||
**could also be set as IP address eg 192.168.0.0/24 |
|||
**typically used for stand-alone servers, to which access from the Internet is permitted |
|||
*Allow remote administration |
|||
== Strictly for Geeks == |
|||
DIY routers based on ARM CPU have become viable during 2012. |
|||
#have potential to match commerical routers in wattage and acreage |
|||
#*whilst maintaining advantage of frequent software updates |
|||
#require more careful matching of hardware and software |
|||
#*ARM compilations are not as "portable" as x86 compilations |
|||
#**advisable to select hardware having an ARM CPU series matching the compilation |
|||
#raspberry pi is best known hardware example - see [[Raspberry Pi]] |
|||
#*IPFire is the only well-known firewall/router that has reached '''released''' level for it |
|||
#*alternatively, raspbian could be adapted as a firewall/router for it |
|||
It is inadvisable to enable |
|||
[[Category:Technical Info]] |
|||
*Allow printing from the Internet*print via network |
|||
[[Category:Recommendations]] |
|||
[[Image:Cups_admin_home.png]] |
|||
then click "Change Settings" button to save any changes, if necessary |
|||
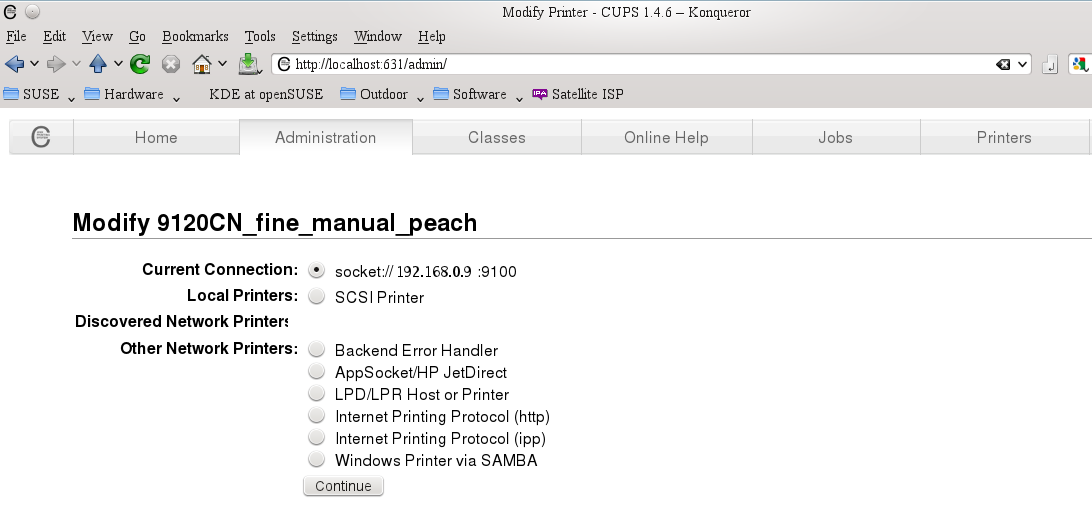
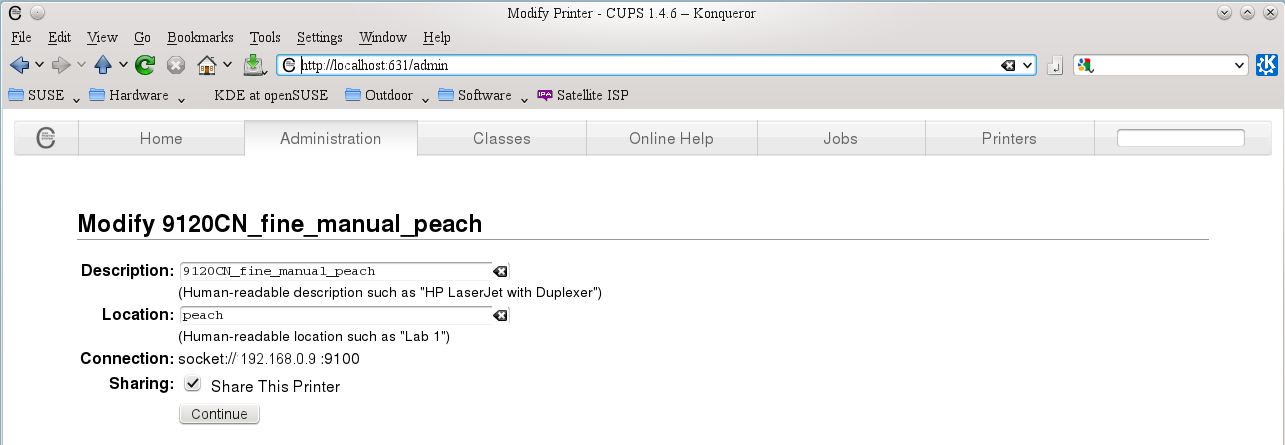
Then click on the "Manage Printers" button in the same tab, select the relevant printer and pull down the "Administration" menu |
|||
#select "modify printer" then click the "continue" button to proceed to its second screen |
|||
[[Image:Cups_printer_network.png]] |
|||
[[Image:Cups_printer_configuration2.png]] |
|||
22 |
|||
#ensure that "share this printer" is checked |
|||
#it will be helpful to make the "Location" the name of the computer controlling this printer |
|||
#click "continue" until the process completes |
|||
**does not require a web browser, which might not be present on a server |
|||
==== Quicktest ==== |
|||
Both computers must be connecting to the local LAN via wired or wireless interface. A quick test is to start a web browser and check that the Internet is accessible. Provided that network access is working: |
|||
#Start a text editor (kate, leafpad etc) |
|||
#*if the application is already running then it may need to be shutdown and restarted to recognize newly available printers |
|||
#Open a new document and type a few words |
|||
#From the file menu, select "Print" |
|||
#Select the relevant printer from the drop-down dialog |
|||
#*which should list all shared printers on the LAN |
|||
#click on the properties/settings button |
|||
#ensure that the key settings are suitable eg A4 paper size, portrait orientation |
|||
#click OK/print |
|||
==== Working Environments ==== |
|||
The following client systems automatically discover network printers, from default configurations |
|||
*Linux Mint 17.3 Mate |
|||
==== Preliminary Troubleshooting ==== |
|||
''1. No printers listed in the print dialog'' |
|||
This problem frequently is the result of a firewall running on one or both computers. Network printing can work only if either: |
|||
*firewalls on each computer allow port 631 through or |
|||
*Ethernet zones are set as "trusted/internal" in the firewalls on each computer |
|||
Only printers powered up will appear in the list |
|||
*confirm that the relevant printer is powered on |
|||
*if it is attached to another PC via parallel or USB cable then that PC must also be powered on |
|||
**(it is not necessary to log in to the sharing PC) |
|||
''2. Print Job accepted but no output on Printer'' |
|||
This can be a result of many possible causes. Some simple checks: |
|||
#is CUPS known to be installed and working on the computer from which the text was created ?. |
|||
#Can it print to some printer at its home base ? |
|||
#does a similar print job created on the server computer give output on the printer ? |
|||
''3. Print Job rejected by Server'' |
|||
*possible permissions issue - check thehat: |
|||
**printer is set as "share this printer" on the server |
|||
***follow "modify this printer" dialog |
|||
*possibly incompatible CUPS verions |
|||
**most suitable arrangement is for all machines using CUPS #< 1.6 |
|||
***achievable only by upgrading the complete OS |
|||
***a new version of the driver for '''each''' printer is required at the server end, to support PDF print jobs |
|||
***if a binary driver, from the manufacturer, was previously used, check whether a driver is now included in CUPS or, failing that, whether an updated driver can be obtained from the manufacturer |
|||
***following the upgrade, follow the "modify this printer" dialog for '''each''' printer and select the most recent PPD file. |
|||
**on older installations, it might be necessary to keep all machines at CUPS version #< 1.5.4 |
|||
If all else fails, then the CUPS Administration page has a button "View Error Log". Text towards the end of that file may give some clues. |
|||
=== CUPS <= 1.5.4 === |
|||
With this version, a (different) CUPS browsing module is usually enabled by default. Simpler configuration changes usually suffice. |
|||
At the server end, browse to |
|||
https://localhost:631/admin |
|||
and activate radio buttons to: |
|||
*Share printers connected to this system |
|||
At the workstation/client end, browse to |
|||
https://localhost:631/admin |
|||
and activate radio button: |
|||
"Show printers shared by other systems" |
|||
[[Image:Cups_admin_home.png]] |
|||
then click "Change Settings" button to save any changes, if necessary |
|||
The troubleshooting tips for version 1.6 and above still apply |
|||
=== Getting Techhnical === |
|||
As a general rule, the print server should have a version not earlier than the client |
|||
*Version 1.5 of CUPS is likely to produce a print job as a PDF file, whereas version 1.3 & 1.4 servers accept only PostScript files |
|||
The above changes can also be implemented via a combination of editing config files and commands via CLI. |
|||
At the server end: |
|||
#ensure that /etc/cups/cups-browsed.conf includes the statements |
|||
*BrowseRemoteProtocols DNSSD,CUPS |
|||
*BrowseProtocols DNSSD CUPS |
|||
*BrowseAllow 192.168.1.0/24 (or network address your LAN, if not this) |
|||
#Log to a terminal as root and execute: |
|||
<nowiki># systemctl cups-browsed.service enable</nowiki> |
|||
<nowiki># systemctl cups-browsed.service start</nowiki> |
|||
At the client end: |
|||
#ensure that /etc/cups/cups-browsed.conf includes the statements |
|||
*BrowseRemoteProtocols DNSSD,CUPS |
|||
*BrowseProtocols DNSSD CUPS |
|||
*BrowseAllow 192.168.1.0/24 (or network address your LAN, if not this) |
|||
#Log to a terminal as root and execute: |
|||
<nowiki># systemctl cups-browsed.service enable</nowiki> |
|||
<nowiki># systemctl cups-browsed.service start</nowiki> |
|||
Save changes |
|||
It will then be necessary to use the Admin tab and select "manage printers" -> "Modify Printer", then modify '''each''' printer to == Situation ==be shared by ticking the box "Share this Printer" |
|||
Often the above steps suffice to make printers visible to a client machine. If not, then the following additional steps might be required, at the '''client''' end: |
|||
Use "Control Panel" to set the following, if available (exact terminology will vary): |
|||
*print via network |
|||
*allow printing to local network only eg 192.168.0.0/24, for non-portable machines |
|||
== Getting Techhnical == |
|||
The above changes can also be implemented via a combination of editing config files and commands via CLI. |
|||
At the server end: |
|||
#ensure that /etc/cups/cups-browsed.conf includes the statements |
|||
*BrowseRemoteProtocols DNSSD,CUPS |
|||
*BrowseProtocols DNSSD CUPS |
|||
*BrowseAllow 192.168.1.0/24 (or network address your LAN, if not this) |
|||
#Log to a terminal as root and execute: |
|||
<nowiki># systemctl cups-browsed.service enable</nowiki> 2 |
|||
<nowiki># systemctl cups-browsed.service start</nowiki> |
|||
At the client end: |
|||
#ensure that /etc/cups/cups-browsed.conf includes the statements |
|||
*BrowseRemoteProtocols DNSSD,CUPS2 |
|||
*BrowseProtocols DNSSD CUPS |
|||
*BrowseAllow 192.168.1.0/24 (or network address your LAN, if not this) |
|||
#Log to a terminal as root and execute: |
|||
<nowiki># systemctl cups-browsed.service enable</nowiki> |
|||
<nowiki># systemctl cups-browsed.service start</nowiki> |
|||
=== Strictly for Geeks === |
|||
= Bootable Media = |
|||
== USB == |
|||
USB devices either "thumb" drives or card readers, usually for SD or microSD cards, have several advantages for booting OS: |
|||
*generally much faster than DVD |
|||
*bootable from UEFI firmware, whereas DVD might not be |
|||
*higher capacity |
|||
*reusable |
|||
Special techniques are required to prepare bootable USB devices. |
|||
== For General Users == |
|||
if the ISO image has been prepared as an '''isohybrid''', then the following tools can readily put it on USB device: |
|||
*http://wiki.rosalab.com/en/index.php/ROSA_ImageWriter |
|||
**this tool is also available for MacOS and Windows |
|||
*https://en.opensuse.org/SDB:Live_USB_stick#Using_SUSE_Studio_Image_Writer |
|||
A previously popular tool was "unetbootin". However this '''breaks''' isohybrids and should be used only with non-hybridised ISO. |
|||
== Getting Techhnical == |
|||
It is now possible to put multiple bootable OS on a single USB device and then boot any from UEFI or non-UEFI firmware. This requires working knowledge of the boot parameters as well as running a number of command line programs. Detailed instructions are at: |
|||
---[[-[[User:Rpeters|Rpeters]] 18:02, 18 August 2012 (EST)]] |
|||
--[[User:Rpeters|Rod]] 09:05, 7 October 2013 (EST) |
|||
--[[Category:Technical Info]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 21:10, 2 February 2017
Projector
Be aware that projectors and monitors have two fundamental differences as external displays
- The majority of projectors, particularly those oriented to "home theatre" are still manufactured with 4:3 ratio display generators
- projectors have many fewer megapixels than do laptops and medium to large monitors
For General Users
Virtually any computer having two display outputs can be made to drive two displays (whether monitor(s) or projector(s) - after a fashion
- occasional users should get adequate result by following the simple guidelines below
- regular users might want to follow the more technical guidelines to try to optimise the displays somewhat
Now the bad news: The potential combinations of hardware and software capabilities are huge.
Additionally, flat panel displays, whether generated via LCD, LED or DLP, produce clearest display only at their native resolution
Projectors for Presentations
Image clarity is paramount for still images as used with presentations
- the human eye cannot resolve high resolution images at the distance typically used with projection screens
- ascertain the aspect ratio of the projector
- if documentation is not available, the ratio of the plain, white image produced when a computer is not connected is a good guide.
- ascertain the native resolution of the projector. In the absence of documentation:
- 1024 x768 is typical for 4:3 ratio projectors
- 1280 x 800 is typical for 16:10 ratios
- 1280 x 720 is typical for 16:9 ratios
- from the computer's Control Panel go to Display and set:
- resolution to same a projector
- tick the box "duplicate/clone these displays"
- click "save" and the desktop should be duplicated on the projector
Display on the laptop/PC will be less than optimum
- "wide-screen" displays may have unlit areas at sides of display
- may be less clear as a result of lower resolution
The above are unavoidable compromises to obtaining clearest display on the projector
Common Problems
- display on the projector is a plain desktop wallpaper without icons or windows for apps
- This is caused by not having the displays duplicated
- revisit Display setup on the computer
- "wide-screen" display on a 4:3 ratio projector
- this is a faulty configuration, which results in less clear display and needs to be corrected
- revisit Display setup on the computer
- if still not corrected, this likely results from default settings in the projector
- activate projector's on-screen display
- navigate to aspect ratio
- change from "auto" or 16:9 to 4:3
First the good news: Virtually any computer having two display outputs can be made to drive two displays (whether monitor(s) or projector(s) - after a fashion
Now the bad news: The potential combinations of hardware and software capabilities are huge.
- occasional users should get adequate result by following the simple guidelines below
- regular users might want to follow the more technical guidelines to try to optimise the displays somewhat
Be aware that projectors and monitors have two fundamental differences as external displays
- The majority of projectors, particularly those oriented to "home theatre" are still manufactured with 4:3 ratio display generators
- projectors have many fewer megapixels than laptops and medium to large monitors
Projectors for Presentations
Preliminary Configuration for Laptops
Projectors for Presentations
Projectors for Home Theatre Use
The majority are still 4:3 native ratio
- but have the capability to accept 16:9 ratio input, typically to support movies
- many default to this ratio and require no reconfiguration
- will display 16:9 ratio input via "letterboxing", ie blanking out the top & bottom 100 or so rows of pixels and displaying image in reduced size
- uses more than the native number of pixels and causes some reduction in image clarity
- which is not significant for movies
- but noticeable with still images (as in presentations)
Up-market projectors are now being manufactured with 16:9 ratio display generators
Getting Technical
Be aware that 3 ratios are in common use for displays - 4:3 and 16:9 for consumer grade devices plus business grade monitors & projectors that support the 16:10 wide-screen ratio
- better quality 16:9 and 16:10 displays might present the complete, alternative image correctly via blanking some rows or columns of pixels with slight "letterboxing" or blank right & left margins
- others will distort the image slightly to occupy the full visible area
All digital displays, whether LCD, LED, Plasma or DLP provide the sharpest image only at their native resolution
Linux & iOS support different resolutions on the two displays
- low end hardware might not support this well, if at all
- if the resolutions selected have differing vertical resolutions on the two displays, then the bottom panel used by many desktops will be absent on the shorter display
- might need to compromise with either
- identical vertical resolutions or
- setting the primary display to the higher vertical resolution
- might need to compromise with either
Strictly for Geeks
For General Users
The idea of having both Windows and Linux installed on a computer and being able to select one at boot time appeals to many who are trying, or migrating to, Linux.
- Windows own bootloader cannot boot Linux
- a Linux bootloader must be used with dual-booting
The better known Linux distributions will set this up automatically, during installation to a single hard disk drive in the computer
- It is likely to cease functioning following the next update of Windows and
- restoring dual-boot requires Getting Technical
Keep at least one emergency boot medium handy. See Emergency_Boot - Including for Dual-Boot
Getting Technical
The above problem can usually be obviated by having additional hard disk(s) in the computer. This is not an expensive option, given current HDD prices.
USB Drive
Pros
- easily added
- no change to internal HDD
Cons
- Linux relies on the absolute order of storage devices detected by the computer's firmware
- plugging in (say) a uSB memory drive, may upset the booting
- many bootloaders will identify partitions via UUID, to overcome this limitation
Internal HDD
- ensures permanent order of drives
Installation
- mainstream Linux will allow installation to== Strictly for Geeks == a second HDD
Selecting Boot Device
The selection of "drive" and hence OS is done at POST stage and depends on type of firmware in the computer
see Booting from Removable Media
Strictly for Geeks
- the bootloader must also be installed to the second HDD, in this technique
- can require "drilling down" the installation options
--Rpeters11:28, 24 August 2012 (EST)
--
Bootloaders
Elilo
Only for computers having EFI firmware
Fairly simple and reliable
- but requires a running Linux to generate its config file, in advance
GRUB Legacy (aka 0.97 )
A simple, reliable bootloader, although being phased out and no longer maintained. Use situations:
- have only Linux on /ext(n) partitions and (maybe) Windows
GRUB (aka GRUB 2 )
GRUB 2 is now the most frequently used bootloader in Linux, but has many remaining issues. Some work-arounds:
"on-the-fly" Mode
GRUB 2 relies on a pre-defined config file /boot/grub(2)/grub.cfg. If this is not located, for any reason, GRUB 2 may boot to a grub> prompt. To boot from here use the following commands, substituting relevant drive and partition numbers:
- grub> set root='hd0,gpt10'
- grub> linux /boot/vmlinuz root=/dev/sda10
- grub> initrd /boot/initrd
- grub> bootBlockquote</blockquote
notes
- drive numbers start from 0
- must specify whether partitioned mbr or gpt
- set root refers to location of partition containing /boot for the operating system to be booted
- which will often also be the root file system for Linux
- or merely the system partition for Win
- partition numbers start from 1 (unlike in GRUB legacy)
- this procedure is easiest if kernel & initrd have easily remembered names
- either soft-link generic names or
- press TAB to see possible names
- ctrl-x or F10 may be pressed in lieu the "boot" command
The above procedure may be modified to cater for the situation where the menu is presented but the desired OS is not included or fails to boot. either
- press e to edit a menu item or
- press Esc to get to command line, then proceed as above.
Menu mode
See GRUB 2 downloadable manual or use "info grub2" to obtain details. Consistent themes amongst various documentation for GRUB 2 are that:
- it is unreliable beyond the basics
- OS-probe module is particularly so
- not putting bootstrap in MBR (protective MBR in case of GPT) will
be problematic
Indeed, "info grub2" recommends avoid all automated installs & configs by distro. Instead, manually grub2-install then write a simple, static /boot/grub2/grub.cfg. See below for outline of this procedure.
As of Jan 2014 and following application of two patches to GRUB in openSUSE 13.1, its GRUB has been brought to ver 2.00-39.4.1. The automated process works well enough for most Linux plus Windows
It failed to find ArchLinux - which uses unusual names for kernels & initrd. Simple work-around for that is to add a 90_persistent section at the end of /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
### BEGIN /etc/grub.d/90_persistent ###
menuentry 'ArchLinux (<your descriptor>) { set root='hd<n>,gpt<n>' linux /boot/vmlinux-linux root=/dev/sd<x><n> initrd /boot/initramfs-linux.img }
### END /etc/grub.d/90_persistent ###
Essentially, the 90_persistent section gets copied verbatim during any subsequent manual or automated run of grub2-mkconfig. Note that this feature might be unique to openSUSE
The curly braces are essential and enclose GRUB2 commands.
This was for a HDD partitioned GPT. replace partition number with mbr<n> if applicable.
Multiple menuentries could be put in 90_persistent to cope with multiple Linuxes.
�
It's also possible to add an entry by pressing "c". In this mode only the 3 commands are input, followed by a fourth command 'boot'CTL-x at the Someone asked how to increase the font size in boot menu. The manual grub.cfg essentially does that by using whatever font will fit on the http://www.pcug.org.au/info/index.php?title=User:Rpeters&action=submit#on in GRUB legacy. press 'e' to edit an entry.
It's also possible to add an entry by pressing "c". In this mode only the 3 commands are input, followed by a fourth command 'boot'CTL-x at the Someone asked how to increase the font size in boot menu. The manual grub.cfg essentially does that by using whatever font will fit on the default screen resolution. Alternatively, one could try to make sense of the "loadfont" parameters in /etc/grub.d/00_header.
Wheras GRUB legacy uses similar syntax in command and menu mode, GRUB 2 uses somewhat different syntax in the two modes.
Rescue mode
An ISO image can be prepared, that is tailored to the OS on a specific computer. See above documentation for details on preparation of this image. It can be tested by "dd" to a USB memory device.
ReFind
Only for computers having EFI firmware
- a CD can be downloaded, to test, if uncertain of firmware
default screen resolution. Alternatively, one could try to make sense of
the "loadfont" parameters in /etc/grub.d/00_header.
Wheras GRUB legacy uses similar syntax in command and menu mode, GRUB 2 uses somewhat different syntax in the two modes.
Rescue mode
An ISO image can be prepared, that is tailored to the OS on a specific computer. See above documentation for details on preparation of this image. It can be tested by "dd" to a USB memory device.
ReFind
Only for computers having EFI firmware
- a CD can be downloaded, to test, if uncertain of firmware
Syslinux
A proven bootloader, that continues being developed and maintained. Main limitations:
- can't directly boot programs on other than its own partition, resulting in the need for work-arounds:
- either chain load all but one OS or
- put the boot code for each OS in a different sub-directory on the syslinux partition
DOS USB
For General Users
Purpose
The main requirement for a USB memory device that boots to DOS operating system arises when a BIOS/Firmware update of a computer is required.
It is advisable to use a new, or little used memory device, because any error in reading the BIOS/Firmware code during the actual update is likely to result in an unusable computer. USB "thumb" drives could be used. SD cards, which can be removed and stored in a secure place, might be more applicable.
Procedure
HP provide two techniques for producing DOS USB sticks. Both place utility software on a Windows computer, in order to generate the bootable stick - see "Getting Technical" below, if Windows is not available.
Instructions are provided on the HP support site for installing these utilities to Windows and creating bootable USB stick(s)
- HP's generic utility HPUSBFW is not self contained but is more flexible.
- it produces a mimimal DOS bootable USB stick containing only nnnDOS.SYS & COMMAND.COM
- the user can then add relevant firmware and flashing utility
- although it has an option for formatting to FAT 32 only FAT actually works
- requires one of HP's "Softpacs" (firmware updates) for one of their recent commercial notebooks, from which to obtain the Windows utility program, plus
- also requires FreeDOS (which can be downloaded at no cost in the form of fd11src.iso from http://www.freedos.org/download/)
- those wanting to upgrade the firmware in a HP computer might find the second tool more suitable. HP provide some of their firmware updates as Windows dotEXE files, which:
- install a utility program to Windows and then have facility called ROMPAQ for creating a bootable DOS on a USB device of not greater than 2 GB (FAT 16)
- automatically adds the firmware and flashing utility to the USB stick
- the naming convention for these files is SPnnnnn.exe
Note that in order to use the former, generic technique, general users would need to burn the above ISO image to CD. Those not familiar with ISO images should read http://www.pcug.org.au/info/index.php/Using_dotISO_Files
The step of burning the ISO image can be avoided - see "Getting Technical" below
Getting Techhnical
The techniques above contain the Windows version of Syslinux in the Windows software package and install the former as a bootloader on the USB device. The Syslinux bootloader can also be added to a USB memory device via Linux. Generic instructions are at the following site, from which (superceded versions of) the code are also available
http://goebelmeier.de/bootstick/
The following would need to be downloaded to obtain up-to-date software:
http://www.freedos.org/download/fd11src.iso
https://www.kernel.org/pub/linux/utils/boot/syslinux/6.xx/
Syslinux will already be installed on many Linux systems. However, Ubuntu and openSUSE might produce a USB stick that invokes graphics at boot time and it is undesirable to have superfluous code on a device that will be used for firmware upgrades.
FreeDOS supports FAT 32 and consequently the above procedure should also work on FAT 32 formatted sticks of > 2 GB capacity. PRINTING VIA NETWORK
PRINTING VIA CUPS
Overview
CUPS is not applicable to Windows. Windows users see Printing via Network
CUPS now the default print sub-system in most Operating Systems - Android, ChromeOS, MacOS, Linux and BSD.
Its use can enable printing over a LAN to be achieved relatively simply, often requiring:
- no additional installation of software or "drivers"
- only simple configuration changes
Applicability
Android & iOS
Typically these require an App to be downloaded from the relevant Store and connect with WiFi enabled printers.
Linux & OSX
Both use CUPS and can be configured as below.
For General Users
Definitions
Those acquainted with client/server model can skip to sub-item "CUPS Versioning Issues"
- "client computer" means the computer/device from which the print job will be generated
- it must have CUPS client installed, which is the default condition for Max OSX and Linux
- it need not have any printer drivers installed
- indeed, it is less confusing if it does not
- "server computer" means the computer controlling the printer. It can be:
- for network printers, which are connected directly to a network, any computer on the network, having the relevant CUPS print drivers installed
- network may be wired, WiFi or bluetooth
- it is perfectly acceptable to configure several computers to use a particular network printer
- for USB/parallel attached printers, the computer to which the printer is attached
- it must have CUPS server installed, which is the default condition for Max OSX and Linux
- the relevant printer must appear in its "Printers" list, and be working
- the computet must be posered on, to enable printing, although logon won't usually be required .
Prerequisites
This guide assumes that CUPS is installed and generally functioning on both computers. The screen shots are from CUPS version 1.4.x/1.5.x. Versions 1.6 et seq have similar menus, but fewer options, with some changes having to be effected via computer's Control Panel instead.
CUPS Versioning Issues
Firstly it is essential to ascertain which release of CUPS is in use, because versions 1.6 and later are largely incompatible with earlier releases. If uncertain, then on each machine involved in the network printing browse to:
https://localhost:631/admin
the release number should be displayed in the title bar
- CUPS <= 1.5.4 uses substantially different process from 1.6 and later
- printing between machines mixing these versions is complicated. see below for guidelines, if unavoidable
- as CUPS <= 1.5.4 is now used mainly in older OS, there is a case for upgrading the OS on such machines to a current release.
- it is not feasible for General Users to upgrade the version of CUPS without upgrading the whole OS
- CUPS 1.6 and later
- Devices sold by Apple Inc can deploy proprietary extensions to CUPS. Consequently, some features may not work as expected, if the print job is sent to a printer that is controlled by another version of CUPS
As a general rule, the print server should have a version not earlier than the client
CUPS mixed networks <= 1.5.4 plus 1.6 et seq
Network printing in this environment is more complex. For a guide to procedures see: http://doc.opensuse.org/release-notes/x86_64/openSUSE/Leap/42.1/
Sample screen images displayed in the following sections are similar for CUPS 1.4 and later.
CUPS 1.6 and later
Later releases of CUPS impose greater network security. Default settings vary with system and may require some troubleshooting if client and server have different origin.
The following client systems automatically discover network printers, from default configurations
- Linux Mint 17.3
- openSUSE Leap
- openSUSE Tumbleweed
Other environments may require changes For a quick test, from the client computer, open any page in a browser or editor and select "Print"
- if any of the networked printers can be selected then no further configuration is required
- if not then:
Temporary Fix
The following procedure is adequate for portable machines that are away from home base. It might also suffice for other computers that are rarely used to print.
- does not require Admin privileges on most systems
- but does require IP address or host name of the machine sharing printers
- settings cannot be saved
The Print Settings applet is usually accessible from the main menu and typically has the icon at left
Start this applet to get its main window as below
Pull down the Server tab and select Connect, to get the following pop-up dialog
Change the name of the server to hostname
or IP address of that required and click on Connect
From the client computer, open any page in a browser or editor and select "Print"
- if any of the networked printers can be selected then no further configuration is required
- if not then:
Main window should now display all discovered printers on the network
From the client computer, open any page in a browser or editor and select "Print"
- if any of the networked printers can be selected then no further configuration is required
- if not then:
If printers are discovered then any newly opened app eg LibreOffice, browsers, editors etc should be able to select and print to one of the printers
If no printers are discovered then changes in configuration are required, as below
Retained Configuration
Neither of the two tools widely deployed for administering CUPS are able to make permanent changes to printer discovery. Both amend the same underling config files:
- system-config-printer (aka Print Settings)
- the URL https://<localhost or URL>:631
Some of the changes required below need to be made by editing conf files and executing commands at a terminal
Summary of Changes
Several settings might need to be changed to print via network - in summary:
- amend firewall settings, on both ends, if necessary
- firewall on router should not be altered
- set client to use printers shared by another machine on the network
- in many installations this suffices to get printing working via network
- activate cups-browsed service via system services (systemd) on both ends
- only in deployments using this separate service
- set CUPS on server to share printers but only to the local network
- often the default setting
It might pay to configure the client computer first, because other machines are often set to share their printers to the local network.
- must be done via Control Panel or a combination of editing files then executing commands
The Print Settings applet typically has the icon ![]()
From the client computer, use "Control Panel" to set the following, if available (exact menus and terminology will vary):
- firewall on server must have port 631 open
- configure "Printers" to use network printers
- note that in many Control Panel apps this item is merely a link the applet "Print Settings", which does not allow changes to print server to be retained.
In cases where Print Settings is the only tool available:
- temporary changes to select print server can be made from the applet
- permanent changes need to be made manually, as follows:
- modify "system services" (exact terminology will vary)
- enable and activate "cups-browsed"
- not identified as a separate service in some distro (and then not required)
- modify the file /etc/cups/client.conf**does not require a web browser, which might not be present on a server
- on many systems this will not exist by default, but creating it, pointing to a valid IP address that is sharing printers, is usually sufficient to enable the client to use shared printers. Only one line is required in this file:
ServerName <IP address of machine sharing printers>
- one only servername is used
- where multiple appear the last is used
- many systems default to "localhost" or /var/run/cups/cups.sock
- can be retained, provided not the last listed
- does not require a web browser, which might not be present on a server
Some distro are issued as specific desktop (client) or server releases. The desktop releases might not provide for changed settings to be saved. That allows eg a laptop away from its home base to print, without disturbing longer term settings.
From the server computer, use "Control Panel" to set the following, if available (exact menus and terminology will vary):
- firewall on server must have port 631 open
- modify "system services" (exact terminology will vary)
- enable and activate "cups-browsed"
- not identified as a separate service in some distro (and then not required)
- enable and activate "cups-browsed"
From the server computer, use any browser to https://localhost:631/admin
and activate radio buttons to:
- Share printers connected to this system
- using protocols DNSSD & CUPS
- restrict sharing to "Local Network"
- could also be set as IP address eg 192.168.0.0/24
- Allow remote administration
It is inadvisable to enable
- Allow printing from the Internet*print via network
then click "Change Settings" button to save any changes, if necessary
Then click on the "Manage Printers" button in the same tab, select the relevant printer and pull down the "Administration" menu
- select "modify printer" then click the "continue" button to proceed to its second screen
- ensure that "share this printer" is checked
- it will be helpful to make the "Location" the name of the computer controlling this printer
- click "continue" until the process completes
- does not require a web browser, which might not be present on a server
Quicktest
Both computers must be connecting to the local LAN via wired or wireless interface. A quick test is to start a web browser and check that the Internet is accessible. Provided that network access is working:
- Start a text editor (kate, leafpad etc)
- if the application is already running then it may need to be shutdown and restarted to recognize newly available printers
- Open a new document and type a few words
- From the file menu, select "Print"
- Select the relevant printer from the drop-down dialog
- which should list all shared printers on the LAN
- click on the properties/settings button
- ensure that the key settings are suitable eg A4 paper size, portrait orientation
- click OK/print
Working Environments
The following client systems automatically discover network printers, from default configurations
- Linux Mint 17.3 Mate
Preliminary Troubleshooting
1. No printers listed in the print dialog
This problem frequently is the result of a firewall running on one or both computers. Network printing can work only if either:
- firewalls on each computer allow port 631 through or
- Ethernet zones are set as "trusted/internal" in the firewalls on each computer
Only printers powered up will appear in the list
- confirm that the relevant printer is powered on
- if it is attached to another PC via parallel or USB cable then that PC must also be powered on
- (it is not necessary to log in to the sharing PC)
2. Print Job accepted but no output on Printer
This can be a result of many possible causes. Some simple checks:
- is CUPS known to be installed and working on the computer from which the text was created ?.
- Can it print to some printer at its home base ?
- does a similar print job created on the server computer give output on the printer ?
3. Print Job rejected by Server
- possible permissions issue - check thehat:
- printer is set as "share this printer" on the server
- follow "modify this printer" dialog
- printer is set as "share this printer" on the server
- possibly incompatible CUPS verions
- most suitable arrangement is for all machines using CUPS #< 1.6
- achievable only by upgrading the complete OS
- a new version of the driver for each printer is required at the server end, to support PDF print jobs
- if a binary driver, from the manufacturer, was previously used, check whether a driver is now included in CUPS or, failing that, whether an updated driver can be obtained from the manufacturer
- following the upgrade, follow the "modify this printer" dialog for each printer and select the most recent PPD file.
- on older installations, it might be necessary to keep all machines at CUPS version #< 1.5.4
- most suitable arrangement is for all machines using CUPS #< 1.6
If all else fails, then the CUPS Administration page has a button "View Error Log". Text towards the end of that file may give some clues.
CUPS <= 1.5.4
With this version, a (different) CUPS browsing module is usually enabled by default. Simpler configuration changes usually suffice.
At the server end, browse to https://localhost:631/admin and activate radio buttons to:
- Share printers connected to this system
At the workstation/client end, browse to https://localhost:631/admin and activate radio button:
"Show printers shared by other systems"
then click "Change Settings" button to save any changes, if necessary
The troubleshooting tips for version 1.6 and above still apply
Getting Techhnical
As a general rule, the print server should have a version not earlier than the client
- Version 1.5 of CUPS is likely to produce a print job as a PDF file, whereas version 1.3 & 1.4 servers accept only PostScript files
The above changes can also be implemented via a combination of editing config files and commands via CLI.
At the server end:
- ensure that /etc/cups/cups-browsed.conf includes the statements
- BrowseRemoteProtocols DNSSD,CUPS
- BrowseProtocols DNSSD CUPS
- BrowseAllow 192.168.1.0/24 (or network address your LAN, if not this)
- Log to a terminal as root and execute:
# systemctl cups-browsed.service enable
# systemctl cups-browsed.service start
At the client end:
- ensure that /etc/cups/cups-browsed.conf includes the statements
- BrowseRemoteProtocols DNSSD,CUPS
- BrowseProtocols DNSSD CUPS
- BrowseAllow 192.168.1.0/24 (or network address your LAN, if not this)
- Log to a terminal as root and execute:
# systemctl cups-browsed.service enable
# systemctl cups-browsed.service start
Save changes
It will then be necessary to use the Admin tab and select "manage printers" -> "Modify Printer", then modify each printer to == Situation ==be shared by ticking the box "Share this Printer"
Often the above steps suffice to make printers visible to a client machine. If not, then the following additional steps might be required, at the client end: Use "Control Panel" to set the following, if available (exact terminology will vary):
- print via network
- allow printing to local network only eg 192.168.0.0/24, for non-portable machines
Getting Techhnical
The above changes can also be implemented via a combination of editing config files and commands via CLI.
At the server end:
- ensure that /etc/cups/cups-browsed.conf includes the statements
- BrowseRemoteProtocols DNSSD,CUPS
- BrowseProtocols DNSSD CUPS
- BrowseAllow 192.168.1.0/24 (or network address your LAN, if not this)
- Log to a terminal as root and execute:
# systemctl cups-browsed.service enable 2
# systemctl cups-browsed.service start
At the client end:
- ensure that /etc/cups/cups-browsed.conf includes the statements
- BrowseRemoteProtocols DNSSD,CUPS2
- BrowseProtocols DNSSD CUPS
- BrowseAllow 192.168.1.0/24 (or network address your LAN, if not this)
- Log to a terminal as root and execute:
# systemctl cups-browsed.service enable
# systemctl cups-browsed.service start
Strictly for Geeks
Bootable Media
USB
USB devices either "thumb" drives or card readers, usually for SD or microSD cards, have several advantages for booting OS:
- generally much faster than DVD
- bootable from UEFI firmware, whereas DVD might not be
- higher capacity
- reusable
Special techniques are required to prepare bootable USB devices.
For General Users
if the ISO image has been prepared as an isohybrid, then the following tools can readily put it on USB device:
- http://wiki.rosalab.com/en/index.php/ROSA_ImageWriter
- this tool is also available for MacOS and Windows
- https://en.opensuse.org/SDB:Live_USB_stick#Using_SUSE_Studio_Image_Writer
A previously popular tool was "unetbootin". However this breaks isohybrids and should be used only with non-hybridised ISO.
Getting Techhnical
It is now possible to put multiple bootable OS on a single USB device and then boot any from UEFI or non-UEFI firmware. This requires working knowledge of the boot parameters as well as running a number of command line programs. Detailed instructions are at:
---[[-Rpeters 18:02, 18 August 2012 (EST)]]
--Rod 09:05, 7 October 2013 (EST) --